What is a kinship? Describe the types of kinship in details.
Kinship refers to the social relationships derived from blood relations (biological or adoptive) or marriage, which structure society in various cultural contexts.
These relationships play a crucial role in shaping social bonds, obligations, inheritance rights, and community organization.
Here are some key aspects of kinship:
Here we will describe the types of kinship
Types of Kinship
- Consanguineal Kinship
- Affinal Kinship
- Fictive Kinship
Categories of Kin
-
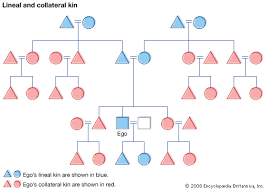
Lineal Kin
-
Collateral Kin
Descent Systems
- Patrilineal Descent
- Matrilineal Descent
- Bilateral Descent
Kinship Terminology
-
Societies have different terminologies for kin based on the importance of relationships.
-
These include:
- Eskimo System
- Hawaiian System
- Iroquois System
Functions of Kinship
- Social Organization
- Inheritance and Succession
- Marriage Rules
- Political and Economic Relationships
Kinship in Modern Societies
While kinship remains an important aspect of social structure, its role has evolved. In modern, industrialized societies, the significance of extended kinship ties has diminished, with more emphasis placed on the nuclear family. Kinship varies greatly across cultures, influencing how societies are organized and how individuals relate to one another.
Kinship systems are integral to social organization and vary across cultures. Some of the key features of kinship include:
Kinship systems are a core aspect of social life and have distinct characteristics that define relationships, roles, and obligations within families and communities. Here are the key characteristics of kinship:1. Universality
2. Social Construction
3. Cultural Specificity
4. Descent
5. Marriage Alliances
6. Inheritance and Property Rights
7. Group Solidarity and Identity
8. Mutual Obligations
9. Endogamy and Exogamy
10. Authority and Power Dynamics
11. Emotional Bonds
12. Regulation of Behavior
13. Kinship Terminology
14. Continuity and Change
Elements of kinship
The elements of kinship are the foundational components that form the structure and function of kinship systems in societies. These elements help organize familial relationships, roles, and social interactions. The key elements of kinship are:
1. Descent
2. Kinship Terminology
3. Marriage
4. Affinal Kinship
5. Fictive Kinship
6. Residence Patterns.
7. Inheritance and Succession
8. Clan and Lineage
9. Mutual Rights and Obligations
10. Socialization and Education
11. Authority and Leadership
12. Taboos and Prohibitions
13. Rituals and Ceremonies
The degree of kinship refers to the measure of closeness or distance between individuals based on their familial relationships. It indicates how many steps or generations separate two people in a kinship network, and it plays an important role in legal, social, and cultural contexts. Different societies use the degree of kinship to determine marriage rules, inheritance rights, social obligations, and family hierarchy. The degree of kinship is calculated based on the generational links between individuals.
Degrees of Kinship
4. Fourth Degree of Kinship
Kinship systems have a variety of important functions and usages across different societies, serving as the foundation for social organization, legal rights, economic exchanges, and cultural practices. Here are the key usages of kinship:
1. Social Organization
2. Regulation of Marriage and Relationships
3. Inheritance and Succession
4. Economic Exchange and Resource Sharing
5. Social Identity and Group Membership
6. Political Organization and Leadership
7. Rituals, Ceremonies, and Religious Functions
8. Care and Social Support
9. Legal and Judicial Functions
10. Kinship in Modern Society

