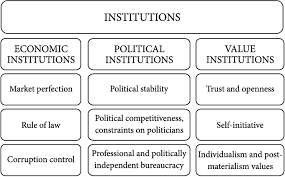
What are Political Institutions?
Political institutions are structures and systems within a society that organize and manage political power, create and enforce laws, and govern the relationships between individuals and the state. They are fundamental to the functioning of a government and its ability to maintain order, provide public services, and protect the rights and freedoms of citizens.
Keys of political institutions
-
The Constitution
-
The Legislature
-
The Executive
-
The Judiciary
-
Political Parties
-
Electoral Systems
-
Bureaucracy
-
Interest Groups
-
Civil Society
-
Local Government
-
International Organizations
State
The state is a form of political entity by which a society is organized under an agency of government that claims legitimate sovereignty over a specified geographical area and has the monopoly of physical force.
Key Characteristics
-
Territory
-
Population
-
Sovereignty
-
Government
-
Recognition
Functions of the state
-
Social control
-
Defense
-
Welfare
-
Law and Order
-
Security
-
Public Services
-
Economic Management
-
Social Welfare
Types of state
-
Sovereign State
-
Nation-State
-
Federal State
-
Confederation
-
Monarchic State
-
Republican State
-
Socialist State
-
Authoritarian State
-
Totalitarian State
-
Theocratic State
-
Failed State
-
City-State
Features of state
The state, as a fundamental concept in political science, possesses several key features that distinguish it from other forms of social and political organizations. Here are the main features of a state:
-
Territory
-
Population
-
Sovereignty
-
Government
-
Legal System
-
Recognition
-
Monopoly on the Use of Force
-
Permanence
-
Public Institutions
-
Nationality or Citizenship
Government
A government is an agency of the state, a complex legal system that has the power and authority to carry out the functions of the state.
It is a formal organization that directs the political life of a society.
Key Components
-
Executive
-
Legislature
-
Judiciary
-
Bureaucracy
Types of Government
-
Democracy
-
Monarchy
-
Authoritarianism
-
Totalitarianism
-
Federalism
-
Unitary System
Relationship Between State and Government
-
Interdependence
-
Continuity
-
Authority
-
Legitimacy
Functions of Government
-
Maintaining Law and Order
-
Protecting National Security
-
Providing Public Services
-
Economic Management
-
Social Welfare and Public Assistance
-
Promoting Social Justice and Equality
-
Upholding the Rule of Law
-
Providing a Stable Political Environment
-
Foreign Relations and Diplomacy
-
Environmental Protection and Resource Management
-
Regulating Commerce and Industry
-
Defining and Enforcing Property Rights
-
Fostering National Identity and Culture
-
Crisis Management and Disaster Response