Describe the forms of kinship. Define “Teknonymy”
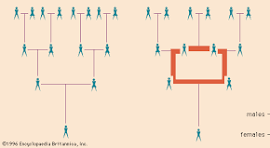
Kinship is one of the important aspects of social structure and one of the basic principles for organizing individuals into social groups, categories and genealogy. Kinship system includes people related through the bond of blood, marriage and includes kindred ones. Marriage establishes social recognition of copulation which is the basic need of life. A man represents one of the basic social institutions, and he believes that the body of kin recognized by him will be different from that of any other man. Broadly, there are two types of kinship which are as follow:-
Consanguineous kinship
Children and their parents, as well as children of the same parents, are called consanguineous kinships by the bond of blood. Thus son, daughter, brother, sister, paternal uncle etc are consanguineous kin. Each of these is related through blood. There are following three types of consanguineal kins:-
-
Lineal kins who are the direct descendants of common progenitors in a vertical line, for instance, grandfather- father- son- grandson.
-
Siblings who are the brothers and sisters i.e. the children of the same parents.
-
Collateral kins who are not related in the single line and are related indirectly through a linking relative, such as father’s brother or brother’s daughter.
Affinal Kinship
Marital relationships connect those individuals as affinal kin. The Affinal kins are not related through the bond of blood. When marriage takes place, both the man and the woman’s families establish new relations with each other.
Define “Teknonymy”
An anthropologist named Edward Tylor coined the term “teknonymy” from a Greek word.
An anthropologist identifies a kin as such by naming another kin. A kin serves as a point of contact between two kins. For example in a traditional Hindu family, a wife does not mention her husband’s name.
Her father is referred to as Guddu.

